The most common joint pathologies are arthritis and arthrosis. Two diseases have many differences, on which the outcome of the disease largely depends.
The correct determination of the disease by a medical specialist serves as a guarantee of effective treatment for the complete restoration of the affected joints. Under the influence of age -related changes, each person has a risk of pathological changes in the joints. The joints are especially affected, which throughout life are subjected to increased load.
Diseases can be a direct cause of articular changes. In order to prevent undesirable consequences from joint diseases, it is necessary not to give diseases to develop, adhering to prevention and treatment measures.
What is arthritis and arthrosis and how they differ
Arthritis and arthrosis are frequent diagnoses in older patients. To understand the differences between these two pathologies, we will consider what arthritis and arthrosis are and what is the difference between them.
Many people confuse arthrosis and arthritis, because they have many similar symptoms:
- aches;
- pain during movement;
- bone deformation;
- swelling;
- redness of the inflamed area;
- a burning sensation in a affected place;
- STATION.
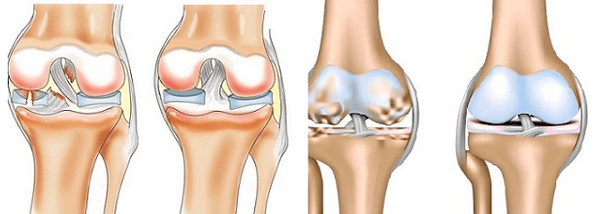
That is why it is necessary to understand these diseases in more detail in order to understand their specifics, to distinguish between symptoms and types of manifestations of the disease.
Arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joints, when enzymes that destroy connective tissue begin to be produced in the body. The synovial shell is affected, where the vessels and nerve endings are located, the composition of the liquid is disturbed, and the cartilage does not receive the right nutrition. Long -term arthritis pours into arthrosis.
Consider the difference in the symptoms between arthritis and arthrosis:
| Symptoms of arthritis | Symptoms of arthrosis |
|
|
Pay attention to the main signs of articular pathologies. Even a slight discomfort in the joints should cause a suspicion of the development of negative processes in cartilage.
Causes
Arthritis is an inflammatory reaction in the joint, which occurs in response to the action of a variety of damaging factors.
Arthrosis, or rather, osteoarthrosis, is also not a separate disease, but a group of completely different states, which are based on a change in all components of the joint: cartilage, bones, ligaments, articular capsule and periarticular muscles.
| Causes of arthritis | The causes of arthrosis |
|
|
However, despite the differences in the symptoms and causes of occurrence, in some cases, arthritis and arthrosis can exist together. For example, with rheumatoid arthritis, frequent exacerbations of the disease are observed in which the joint does not have time to recover. Another example: the joint incorrectly fused after the fracture, which is constantly undergoing trauma. Doctors call such states "Arthroso-Arthritis. "
Diagnostics
To begin treatment of the disease, the correct diagnosis of arthritis or arthrosis is important. It can be carried out using various research methods. Not all patients know which doctor is engaged in joint pathologies, so at the initial stage you can contact a rheumatologist or therapist, and then you will need a consultation of an orthopedist, a surgeon.
Patients must be prescribed a blood test that will demonstrate general changes in the body. If the results of the blood test do not show deviations, then the doctors are inclined towards arthrosis as a preliminary diagnosis.
With an increase in the rate of settlement of red blood cells in the blood plasma, rheumatoid arthritis is suspected, since there is a clear indication of the inflammatory process. Typically, the indicator increases above 25 mm/h. The joint pain, intensifying at night, will also be an additional confirming feature. In fairness, we note that an increase in ESR is possible with arthrosis, if inflammation has joined it.
An additional argument in favor of rheumatoid arthritis will be an increased amount of leukocytes. They also take blood from the vein to rheumatological samples-the appearance of a special brand-a reactive protein that speaks of inflammation. However, you should not rely only on blood examination, since one of the diseases cannot be determined by this analysis. It is necessary to conduct additional studies, constantly taking into account the presence of an inflammatory factor in the blood.
As additional studies, doctors prescribe to the patient:
- X -ray of the problem area;
- magnetic resonance tomography;
- computed tomography;
- Radioisotopic scanning.
Doctors take into account tests, a carefully collected history and the results of a blood test, after which a particular disease is diagnosed.
Arthritis and arthrosis - how to treat?
Both ailments involve special therapy, without which arthritis passes into a chronic form, and arthrosis deprives of performance.
The general principles of treatment are similar, but the tasks are different:
- with arthritis, the main goal is to relieve inflammation, eliminate painful symptoms, prevent complications to other organs;
- With arthrosis, due to the inability to completely cure the disease, the main therapeutic emphasis is on the relief of pain and stopping dystrophic processes in cartilage.
The complex of medical measures necessarily includes medicines in the form of tablets, ointments, creams, solutions, powders, injections. As auxiliary methods, folk recipes, physiotherapy, and therapeutic exercises are used. In advanced cases, you can not do without surgical intervention.
| Treatment of arthritis | Treatment of arthrosis |
|
|
Treatment of arthrosis is prolonged and complex - in a hospital institution, clinic and sanatoriums. Using physiotherapy exercises, massages, physiotherapeutic procedures. There is an orthopedic correction. With the ineffectiveness of the above, surgical manipulations are carried out - arthrodesis (motionless fixation of the bone compound in a given position) or arthroplasty (restoring joint capabilities).
Arthritis therapy is also carried out comprehensively, depending on the severity of the disease. Physiotherapeutic methods and spa resort treatment are prescribed. Massage is not recommended here, exercise therapy is very rare. In case of complications (inflammation of the perioset bag, rupture of tendons, complex joint deformations), with severe pain and the lack of the effect of drug therapy, surgery is performed. This is the prosthetics of bone joint, complete or partial removal of the joint bag and arthrodesis.
Treatment of arthritis and arthrosis folk remedies
Folk methods are a good assistant in the treatment of arthritis and arthrosis at home. These recipes based on natural components have a predominantly symptomatic effect, used as an additional tool.
| Folk recipes for arthritis | Folk remedies for arthrosis |
With arthritic joint inflammation, you can do:
|
To alleviate the condition with arthrosis will help:
|
All recipes can be used for both diseases, but only after consulting with the attending physician. Home treatment can help, eliminating unpleasant sensations and harm, causing an allergic reaction and exacerbation.
Result
The difference between arthritis and arthrosis is significant. Knowing the characteristics of articular diseases will help the patient control the course of the pathological process, competently use all available methods of treatment. Under the guidance of an experienced doctor, you can cope with any articular pathology.
In order to prevent diseases, attention should be paid to a healthy lifestyle. A balanced meal and systematic physical exercises will increase the life of the joints, and this is necessary to strengthen the whole health.













































